Disc Bulge: Causes, Symptoms, and Effective Relief Options

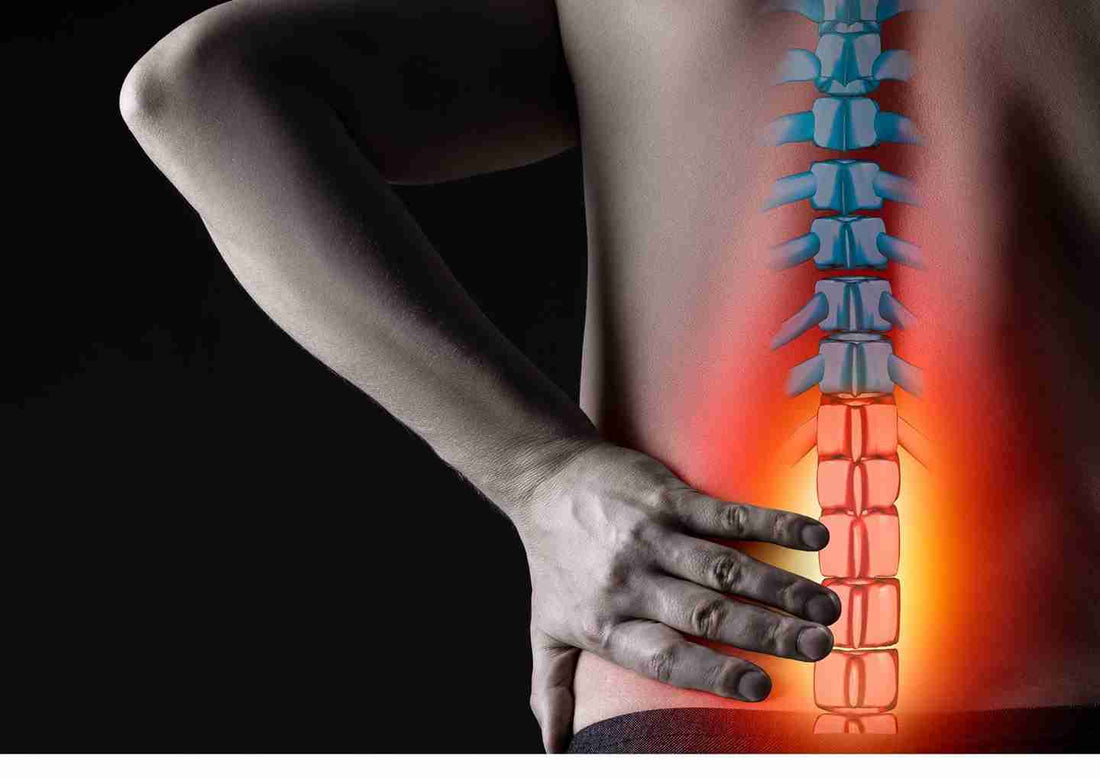
A bulging, or herniated, disk occurs when the spongy center of a disk in the spine pushes out through a tear in the outer, rubbery portion of the disk. Symptoms can include pain and problems with mobility.
Bulging disks, also known as herniated, ruptured, or protruding disks, are usually due to age-related degeneration. Symptoms tend to progress gradually.
Treatment for bulging disks in the back include short and long term options that aim to decompress the spinal canal and ease pain.
This article explains the causes, symptoms, and treatment options for a bulging disk, as well as pictures of a herniated disc and exercises that may offer pain relief.
What is a Disc Bulge
Disks act as cushions between the bones that form the spine. These bones are called vertebrae. Disks have an outer layer of tough cartilage that surrounds softer cartilage in the center. It may help to think of disks as miniature jelly doughnuts, exactly the right size to fit between your vertebrae.
Disks show signs of wear and tear with age. Over time, disks become less flexible. These changes can cause the outer layer of the disk to bulge out. A bulging disk looks a little like a hamburger that's too big for its bun.
When a crack in the tough outer layer of cartilage allows some of the softer inner cartilage to stick out of the disk, these disc bulges (also called herniated discs) become more likely to cause pain. The inner cartilage of the disk sticks out farther and is more likely to irritate nerve roots. The irritation can be from pushing on the nerve or, much more commonly, the herniation causes a painful inflammation of the nerve root.

Symptoms of a bulging disk depend on its severity and location in the spine. Some people may have no initial symptoms. However, with further disk degeneration and herniation, a person may experience the following:
- back pain that worsens with movement, such as when sneezing
- spasms in the back muscles
- sciatica
- weakness and numbness in the legs and feet
- reduced mobility in the legs, knees, and ankles
- decreased bladder and bowel control
- difficulty walking
- reduced coordination
Pain may also radiate to different areas of the body, such as the arms or rib cage.
Bulging disks result from a change in the consistency of the gel in the disk center. A reduction in gel quality can cause the disk to become compressed and start to bulge.
The gel in the spinal disk naturally wears away over time. A bulging disk usually results from aging, but it can also be due to spinal injury, such as the result of a car accident. An injury could also cause symptoms to become more severe.
Risk factors for a disc bulge include:
- engaging in some types of physical activity, especially if they involve repetitive movements
- having a job that involves lifting heavy objects
- obesity
- long distance driving frequently
- sedentary lifestyle with limited physical activity
- smoking, as it may accelerate degeneration by reducing the oxygen supply to the disk
- lifting weights improperly (especially in gym)
Treatments for a bulging disk will depend on its severity and location. Following are some of the recommended ways to reduce the discomfort:
- Bed rest: Bed rest for 1–2 days may offer some pain relief. However, people should reintroduce controlled, slow physical activity after this.
- OTC medicines: These include nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) to reduce pain and inflammation.
- Physical therapy: Physical therapy can help to strengthen the muscles in the lower back and abdomen.
- Steroid injections: Steroid injections into the space around the nerve may offer short term pain relief when other treatment options to not work. However they are costly, and often don't solve the issue permanently
- Surgery: Surgery for a herniated disk may improve pain and mobility, but is typically a last resort treatment option.
Exercises
The following are examples of exercises and stretches that help with a disk bulge in the lower back:
1. Cobra Stretch

A person should follow these steps to complete a cobra stretch:
- Lie on the stomach on the floor, with the hands on the ground and just above shoulder level.
- Keeping the hips on the floor, raise the upper body, supporting it with the elbows.
- Hold for 10–15 seconds and slowly lower the upper body back to the floor.
- Gradually build up to 30 seconds and repeat ten times.
2. Cat Cow

The following steps explain how to complete a cat-cow stretch:
- Begin on the hands and knees, with the hands directly under the shoulders and the knees right under the hips.
- Breathing in slowly, draw the chest forward and the shoulder blades down the back body. Keep the neck long and hug the low belly in.
- Exhaling slowly, press the floor away, round the upper back, and gently release the head and neck.
- Repeat ten times.
3. Forearm Plank

To complete a forearm plank, people should:
- Start by lying on a mat, face down, with the forearms on the mat.
- Using core strength, lift the body until you are resting on the forearms and toes.
- Hold for 20–30 seconds.
- Release slowly.
- Repeat five–ten times.
4. Knee Hugs

A person can use the following steps to carry out knee hugs:
- Lie on the back, with the knees bent and the feet on the floor.
- Grasp one knee with both hands and pull it toward the chest.
- Hold, release slowly, and repeat with the other leg.
- Repeat five times.
5. Back Stretch

The following steps describe a back stretch:
- Lie on the back, holding both knees toward the chest, with the sacrum on the floor.
- Move the head forward until there is a stretch across the lower back, but do not strain.
- Repeat five times.
Preventing a bulging disk is not always possible, as disk gel naturally degrades over time. However, people can take the following steps to prevent a bulging disk from becoming severe:
- reach or maintain a moderate body weight to reduce pressure on the vertebrae
- keeping physically active to strengthen the muscles surrounding the spine
- staying flexible and taking breaks to stand and stretch when sitting for long periods
- practicing proper posture to reduce stress on the spine
Below are some common questions about a disc bulges.
1. Do disk bulges heal on their own?
Most herniated disks will heal within a few weeks. Home remedies, including gentle exercise, OTC pain relief, and proper lumbar support can help treat a bulging disk. However, people should speak with a doctor if symptoms do not subside.
2. What should you not do with a bulging disk?
Prolonged bed rest, improper lifting, and excessive or strenuous exercise may worsen bulging disk symptoms.
Bulging disks occur when the spongy center of a disk in the vertebrae pushes out through a tear in the outer, rubbery portion of the disk.
The primary cause of bulging disks is aging. However, it can also occur after an injury. A bulging disk can push against the spinal cord and nerve roots, leading to severe pain and problems with mobility.
Treatment may include a combination of OTC pain medication, physical therapy, and self-care. In severe cases, a person may need surgery.
Learn More About Zanskar Health
If you have joint pain, muscle pain or headaches that makes it hard to move, Zanskar offers the most advanced full stack pain relief solutions for you.
Now available to purchase, Zanskar® pain-care range have unique bio-active formulations. It provides lasting relief from muscle and joint discomfort that you can feel good about. Get your fix before stocks run out - buy now.
You can also gain access to therapeutic exercises and stretches for your condition by downloading the Zanskar Health physiotherapy mobile app. Additionally, you’ll have a personal care team to guide, support, and tailor our program to you, including behavioral and nutritional coaching.
Download our mobile app here 👉 download and track your exercise streak.
Medical Review: This article is written and medically reviewed by Dr Nishtha Mittal (Senior Health Content Editor at Zanskar Health). This article and its contents are provided for educational and informational purposes only and do not constitute medical advice or professional services specific to you or your medical condition.